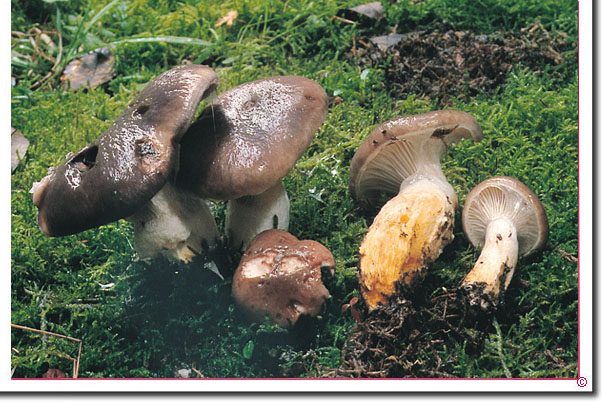
Das Kuhmaul Gomphidius glutinosus wurde 1774 von Jacob ChristianSchaeffer in Fung. bavar. palat. nasc. (Ratisbonae) 4: 17 als Agaricus glutinosus beschrieben.
Elias Fries hat dieses Basionym 1838 umkombiniert zum heute gültigen Gomphidius glutinosus (Schaeff.) Fries, in Epicrisis systema mycologicae: 319 (Stand 1.11.2015 9.34 h)
Synonyme:
Agaricus adhaerens J.F. Gmel., Systema Naturae, Edn 13 2(2): 1403 (1792)
Agaricus fuscus Batsch, Elench. fung., cont. prim. (Halle): 47 (1783)
Agaricus mitratus J.F. Gmel., Systema Naturae, Edn 13 2(2): 1403 (1792)
Agaricus velatus Withering, Bot. arr. Brit. pl., Edn 2 (London) 3: 290 (1792)
Agaricus viscidus var. atropunctus Persoon, Syn. meth. fung. (Göttingen) 2: 292 (1801)
Cortinarius viscidus fa atropunctus (Persoon) Gray, Nat. Arr. Brit. Pl. (London) 1: 629 (1821)
Gomphus glutinosus (Schaeff.) Paul Kummer, Führ. Pilzkunde: 93 (1871)
Leucogomphidius glutinosus (Schaeff.) Kotl. & Pouzar, Česká Mykol. 26(4): 219 (1972)
Volksnamen:
Deutsch: Kuhmaul, Großer Gelbfuß, Gelbfuß, Großer Keilpilz, Großer Schleimpilz, Rotzer, Schafsnase, Schmierling .
Englisch: Slimy Spike .
Französisch: Gomphide glutineux, Pied de rhubarbe (Rhabarberfuß) .
Niederländisch: Slijmige spijkerzwam .
Dänisch: Grå Slimslør .
Norwegisch: Sleipsopp .
Schwedisch: Citronslemskivling .
Finnisch: Limanuljaska .
Spanisch: Cama de perdiu mucosa .
Italienisch: Chiodello .
Ungarisch: Barna nyálkásgomba (Brauner Schleimpilz) .
Slowakisch: Sliziak mazlavý.
Slowenisch und serbisch: Veliki slinar .
Rumänisch: Băluşca molidului .
Tschechisch: Slizák mazlavý .
Polnisch: Klejówka świerkowa, Klejówka kleista.
Lettisch: Eglaines zeltkāte .
Litauisch: Gličioji geltonpėdė .
Estnisch: Pihkane liimik .
Wallonisch: Glumiant clô, Gomphide gluant, Gloumiant clå .
Bekanntheitsklasse: 1
Speisewert (***)
Lebensweise .
. symbiotisch .
. Vorkommen .
bei Fichten
. Größe: m bis l
. Pilzform normal
. Wuchsform .
. gruppenweise .
Hutunterseite
. lamellig .
. Lamellen .
. herablaufend .
. Stiel .
. schleimig .
Sporenpulverfarbe:
schwarz
Verwandtschaft
Ständerpilze
. Basidiomycetes .
Röhrlingsartige
. Boletales .
Röhrlingsverwandte
. Boletaceae .
Schmierlinge
. Gomphidius .
Hier gehts direkt zum Kuhmaul
Gomphidius glutinosus
Speisewert (***)
Lebensweise .
. symbiotisch .
. Vorkommen .
bei Fichten
. Größe: m bis l
. Pilzform normal
. Wuchsform .
. gruppenweise .
Hutunterseite
. lamellig .
. Lamellen .
. herablaufend .
. Stiel .
. schleimig .
Sporenpulverfarbe:
schwarz
Verwandtschaft
Ständerpilze
. Basidiomycetes .
Röhrlingsartige
. Boletales .
Röhrlingsverwandte
. Boletaceae .
Schmierlinge
. Gomphidius .
Hier gehts direkt zum Kuhmaul
Gomphidius glutinosus